P-ISSN: 2394-0530, E-ISSN: 2320-3862
2015, Vol. 3, Issue 2, Part A
Association and root colonization of some medicinal plants with Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi
Tulshi Thapa, Utanka Kumar De, Bishwanath Chakraborty
Twelve medicinal plants belonging to eight different families were selected to study the prevalence of AMF colonization. The plant roots and their respective rhizospheric soil were collected from the Garden of Medicinal Plants, University of North Bengal for AMF analysis and spore assessment per 100 gm of soil. The result showed variation in both AMF colonization and spore percentage. All medicinal plant species studied were found to be colonized by AMF. Highest percent colonization was evident in Justicia adhatoda (95±2.00). Highest spore count was found in Abroma augustum (197.4±9.31). Spore characteristics were studied and tried to identify upto species level based on the available standard keys. Histopathological studies revealed presence of abundant vesicles, thin branched as well as coiled arbuscules along with extra and intra radical hyphae. The present study revealed that the genus of Glomus, Gigaspora, Acaulospora were more predominant. Scutellospora and Entrophospora are least amongst the recovered AMF spores.
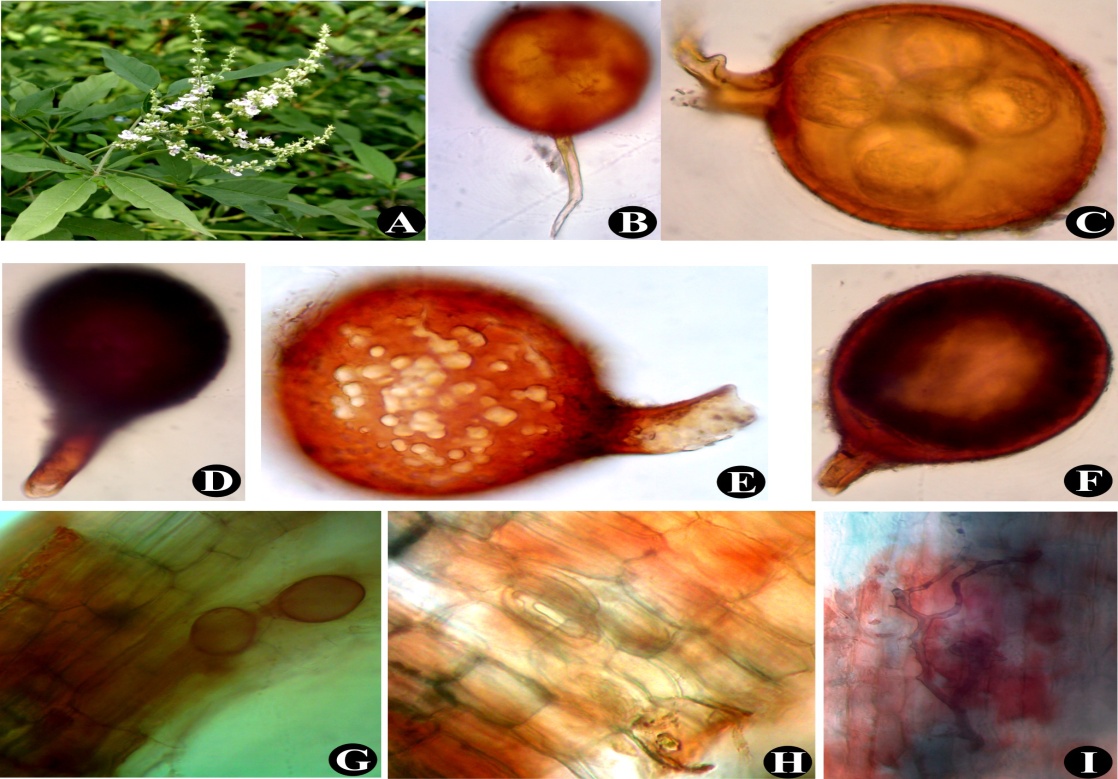
Fig.: Vitex negundo (A); Glomus mosseae (B); Sporocarp of Glomus sp. (C); Glomus constrictum (D); Glomus sp. (E); Glomus sp. (F); Vesicles, arbuscules and Intraradical hyphae (G) to (I)
Pages : 25-35 | 2050 Views | 262 Downloads
How to cite this article:
Tulshi Thapa, Utanka Kumar De, Bishwanath Chakraborty. Association and root colonization of some medicinal plants with Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi. J Med Plants Stud 2015;3(2):25-35.
Related Journal Subscription
Important Publications Links






