P-ISSN: 2394-0530, E-ISSN: 2320-3862
2016, Vol. 4, Issue 3, Part A
Phytochemical analysis and in vitro urolithiatic activity of Peltophorum pterocarpum leaves (DC) Baker
Rahul Jha, Pooja Tahil Ramani, Dhara Patel, Sharav Desai, Dhananjay Meshram
Phytochemicals are responsible for medicinal activity of plant species. Natural products from medicinal plants, either as pure compounds or as standardized extracts, provide unlimited opportunities for new drug leads because of the unmatched availability of chemical diversity. Peltophorum pterocarpum, family Leguminosae is a tree natural to tropical South-Eastern Asia and was brought to Nigeria by immigrants. Continuous research have revealed many chemical constituents isolated from different parts of the this tree to exhibit several biological activities such as antimicrobial activity, antioxidant activity, cytotoxic activity, antiglycemic activity, aldose reductase inhibition activity, cardiotonic activity and choline esterase inhibitory activity. The present study aims at studying the Anti urolithiatic activity of methanolic and aqueous extracts of the leaves of Peltophorum pterocarpum. Results obtained from in-vitro, in- vivo and clinical trials reveal that phytotherapeutic agents could be useful as either alternative or an adjunct therapy in the management of Urolithiasis. Medicinal plants / natural products are more useful for body because they promote the repair mechanism in natural way. been. In this experiment aqueous and methanolic extracts of Peltophorum pterocarpum and standard for dissolving kidney stones- calcium oxalate by an in-vitro model. To check their potential to dissolve experimentally prepared kidney stones- calcium oxalate by an in-vitro model for Peltophorum pterocarpum leaves and cystone as a standard compound collected from market. Phenolic compound isolated from the benzene and aqueous, flavanoids and steroids from aqueous fraction of the seed. Aqueous fractions showed highest dissolution of stones as compare to others. Aqueous fraction was more effective in dissolving calcium oxalate.
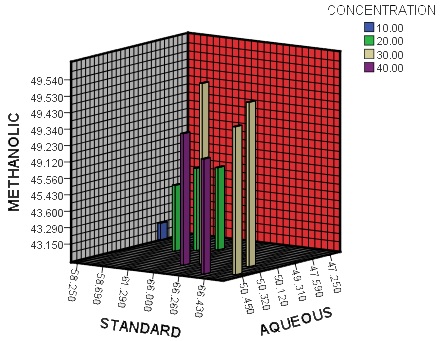
Fig.: Individual Extracts Showing % Dissolution of Calcium oxalate crystals with different concentration
Pages : 18-22 | 2234 Views | 240 Downloads
How to cite this article:
Rahul Jha, Pooja Tahil Ramani, Dhara Patel, Sharav Desai, Dhananjay Meshram. Phytochemical analysis and in vitro urolithiatic activity of Peltophorum pterocarpum leaves (DC) Baker. J Med Plants Stud 2016;4(3):18-22.
Related Journal Subscription
Important Publications Links






