P-ISSN: 2394-0530, E-ISSN: 2320-3862
2013, Vol. 1, Issue 3, Part A
Effect of Deficit Irrigation on Growth, Yield and Volatile Oil Contenton Rosmarinus officinalis L. Plant
Hassan, F.A.S*, Bazaid. S., Ali. E.F (Egypt)
The influence of deficit irrigation on the growth, yield and essential oil content of (Rosmarinus officinalisL.) wasrninvestigated. Three irrigation treatments were applied in this experiment. The first treatment was 100% of the fieldrncapacity as a control. The second and third treatments were received 80% and 60% of the field capacity, respectivelyrnas deficit irrigation treatments. Deficit irrigation significantly reduced growth parameters and relative water contentrnof rosemary plants compared to the control. The volatile oil percentage was increased; however yield was decreasedrnby applying deficit irrigation treatments. The GC results showed that the main components were α-pinene, 1,8rncineol, linalool, camphor and borneol and were affected by deficit irrigation. Chlorophyll content was graduallyrnincreased with increasing irrigation frequency however, carbohydrate percentage increased by deficit irrigationrntreatments. Deficit irrigation, as a possible technique for saving water, can be used to control growth and save waterrnin rosemary cultivation.
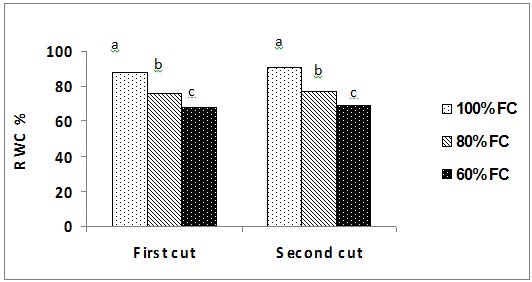
Fig.: Effect of deficit irrigation treatments on relative water content (RWC %) of rosemary plant in the first and second cuts. Bars had different letters are significantly differ for each other according to Duncan multiple range test at P = 0.05.
Pages : 12-21 | 1936 Views | 172 Downloads

How to cite this article:
Hassan, F.A.S*, Bazaid. S., Ali. E.F (Egypt). Effect of Deficit Irrigation on Growth, Yield and Volatile Oil Contenton Rosmarinus officinalis L. Plant. J Med Plants Stud 2013;1(3):12-21.
Related Journal Subscription
Important Publications Links






