P-ISSN: 2394-0530, E-ISSN: 2320-3862
2013, Vol. 1, Issue 5, Part A
Species Specific Changes in Chlorophyll Fluorescence in Deciduous and Evergreen Tree Species Growing Under Short Rotation High Density Energy Plantation in North-Western Himalaya
Gopichand
Diurnal changes in chlorophyll (chl) a fluorescence characteristics of Sun exposed and shaded leaves of somerndeciduous and evergreen tree species growing under short rotation high density energy plantation in north-westernrnHimalaya, during sunny and cloudy days were recorded. Significant reduction in photochemical efficiency ofrnphotosystem (PS) 2 measured as Fv/Fm ratio during period of maximum irradiance was observed in Sun exposedrnleaves of some tree species. The extent of this reduction was actually a function of various plant processes. Thernobservations were recorded in 3 years for different selected months and time. The maximum photoinhibition wasrnrecorded in between 12.00 noon to 14.00 hrs. Among the deciduous species, Salix tetrasperma showed thernmaximum reduction (46%), whereas Grevillea robusta showed least decline (< 31%) in the Fv/Fm ratio in 1994. Inrn1995, some species showed maximum reduction 60%, and other species like Trewia nudiflora, Toona ciliata,rnMorus alba and Melia azedarach showed least decline (15 to 19%) in the Fv/Fm ratio. In 1995, Salix tetrasperma atrn14.00 hr. showed maximum reduction (34%), while at 9.00 hr, 11.00 hr and 16.00 hr it showed least decline in thernFv/Fm ratio. viz, Salix tetrasperma and Eucalyptus hybrid. Some species as Salix tetrasperma were mostrnsusceptible to high irradiances. Prolonged exposure of these plants to high irradiances resulted in lesionrndevelopment on leaves characterized by reduction in pigment content and Fv/Fm ratio. Plant species withrnconsiderable midday decline in Fv/Fm ratio showed (i) slight but significant rise in initial fluorescence (Fo), (ii)rnpronounced decrease in Fm value, and (iii) significant reduction in area over the curve between Fo and Fmrnindicating the pool size of electron acceptors on the reducing side of PS2. The depression in Fv/Fm ratio thoughrnreversible could not be alleviated even after watering the plants. No reduction in Fv/Fm was observed in shadernleaves of the same plants and/or when measurement were taken on cloudy days and morning (9.00 and 11.00 hr),rnand evening (14.00 hrs and 16.00 hr) hours. Hence high solar radiation and high atmospheric evaporative demandrnexisting during summer/draught period could probably be the major contributory factor for this reduction.
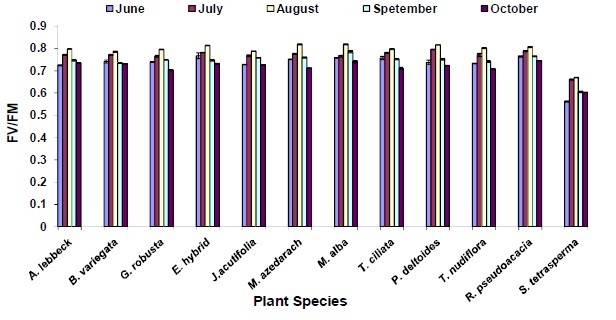
Fig.: The Fv/Fm values of some tree species, recorded between 8.00 hrs to 12.00 hrs and 14.30 hrs to 17.00 hrs in different months, third year of planting.
Pages : 41-50 | 1802 Views | 89 Downloads

How to cite this article:
Gopichand. Species Specific Changes in Chlorophyll Fluorescence in Deciduous and Evergreen Tree Species Growing Under Short Rotation High Density Energy Plantation in North-Western Himalaya. J Med Plants Stud 2013;1(5):41-50.
Related Journal Subscription
Important Publications Links






