P-ISSN: 2394-0530, E-ISSN: 2320-3862
2014, Vol. 2, Issue 2, Part A
Queen of herbs tulsi (ocimum sanctum) removes impurities from water and plays disinfectant role
Babita Labh Kayastha
Tulsi is a Sanskrit word which means “matchless one”. Several medicinal properties have been attributed to the Tulsi plant not only in Ayurveda and Siddha but also in Greek, Roman and Unani systems of medicine. In Ayurveda, Tulsi used as antiasthmatic and antikaphic drugs. It is also used in treatment of fever, bronchitis, arthritis, convulsions etc. Scientific explorations of traditional belief of medicinal properties of Tulsi have got momentum mostly after the middle of the 20th century. Ocimum sanctum (Tulsi or holy basil) has a very special place in the Hindu culture. The present study was focused on evaluation of antimicrobial activity of Ocimum sanctum leaf extract in normal tap water and local river water. The antimicrobial effect was studied with different concentration (100 to 600 mg l-1) of Tulsi leaf extract in tap and river water. In this, 600 mg l-1 concentration of plant extract treated water showed effective antimicrobial activity at 15 to 16 hrs than the other concentration of extract. The 500 mg l-1 of extract treated water showed 95 to 98% antibacterial activity in 14 to 16 hrs. The minimum bacterial concentration (MBC) was observed in 500 and 600 mg l-1 extract concentration. The concentration of the bacterial cells inhibited gradually for an hour was studied by spread plate method.
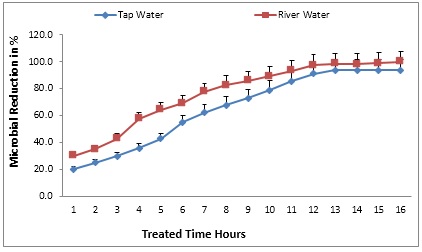
Fig.: Treatment of water samples with 600 mg of Ocimum sanctum extract
Pages : 01-08 | 2013 Views | 257 Downloads
How to cite this article:
Babita Labh Kayastha. Queen of herbs tulsi (ocimum sanctum) removes impurities from water and plays disinfectant role. J Med Plants Stud 2014;2(2):01-08.
Related Journal Subscription
Important Publications Links






