P-ISSN: 2394-0530, E-ISSN: 2320-3862
2015, Vol. 3, Issue 6, Part A
Evaluation of antimicrobial potential of aqueous and alcoholic extract of Triphala against wound pathogens
S Kirubanandan, S Renganathan
The healing of an infected wound is still challenging for regeneration of dermis and epidermis in wound site due to the presence of bacterial pathogens and its metabolites such as collagenase and elastase. These metabolites degrade numerous extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen and elastin at wound site. As a result, the wound closure is delayed. Having existing antibiotic therapy for wound healing past decades, it has many disadvantages such as absence of synergistic activity, cyto-toxicity and then development of antibiotic resistance. Therefore, Phyto-pharmaceutical is the best source for potential antimicrobial agents to eradicate the wound pathogens for faster wound healing. Triphala is a kind of poly herbal Ayurvedic formulation and used for evaluation for antimicrobial action against wound pathogens. The aqueous and methanol extract of Triphala is prepared in Soxhlet extraction apparatus. The dried extract was dissolved in 10% Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) and used to assay the antibacterial potential of these extracts against wound pathogens by minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and disc diffusion assay. This investigation showed susceptibility of wound pathogens including clinical isolated from wound environment to the aqueous and alcoholic extract of Triphala. The disc diffusion assay confirmed clear zone of inhibition for S. aureus (19±1.5 mm) P. aeruginosa (20±1.0 mm) and S. pyogenes (15±1.5 mm) in the case of Alcoholic extract. The aqueous extract showed zone of inhibition around ~12 -14 mm for all bacteria. The MIC of Triphala alcoholic extract against S. aureus as well as P. aeruginosa was found between 3.91–7.81 mg/ml and against S. pyrogenes between 15.6–31.25 mg/ml. The alcoholic extract of Triphala has potent antimicrobial activity against wound pathogens and hence prevents wound infection at the wound site. Additionally, this investigation helps to prepare ointment formulation of Triphala for various wound healing including pressure sores and diabetic ulcers.
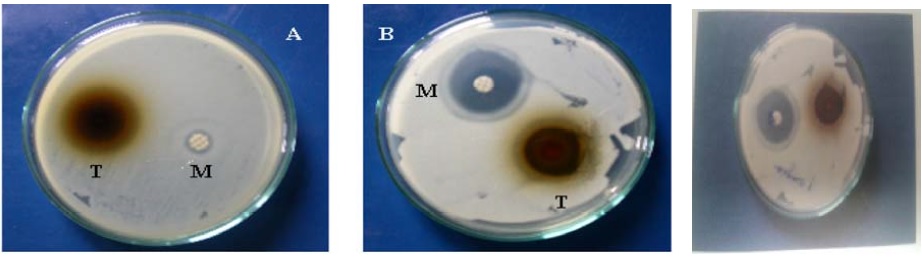
Fig.: Disc Diffusion Assay for Methanol Extract of Triphala against (A) clinical isolates MRSA, (B) S.aureus and (C) Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Pages : 56-59 | 1789 Views | 182 Downloads
How to cite this article:
S Kirubanandan, S Renganathan. Evaluation of antimicrobial potential of aqueous and alcoholic extract of Triphala against wound pathogens. J Med Plants Stud 2015;3(6):56-59.
Related Journal Subscription
Important Publications Links






