P-ISSN: 2394-0530, E-ISSN: 2320-3862
2016, Vol. 4, Issue 1, Part A
Prospective wild edible fruit plants from part of northern Western Ghats (NWG), Mulshi (MS), India
Rani B Bhagat, Mahadev Chambhare, Sandip Mate, Amit Dudhale, BN Zaware
A survey was carried out to document traditional religious information of prospective wild edible fruits consumed by tribal and non tribal communities in Mulshi, a part of Northern Western Ghats (NWG). Forests represent an integral part of the social life of tribal groups and are home to the people who are completely or partly dependent on forests for their livelihood. The communities in Mulshi include “Marathasâ€, "Katkari" "Mahadeo koli" and “Dhangarsâ€. The study area is rich in genetic and species diversity including rare, endemic, endangered and threatened (RET) category species. The wild edible fruits plays fundamental role in human diet and are enriched with macronutrients, microelements, secondary metabolites and have high nutritional value. The fruits are eaten either as a raw in ripe or unripe condition. The total of 109 wild edible fruit plant species belonging to 85 genera and 57 families has been investigated in present research work. The potentialities of these fruits could be explored and utilized for pharmaceutical industry or as an additional fruit crop source in agriculture with high food value and with exceptional medicinal properties.
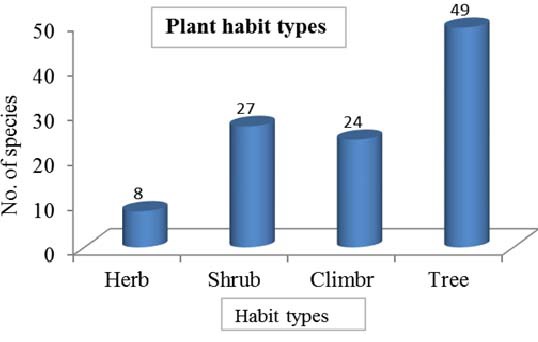
Fig.: Plant habit diversity of wild edible fruits in Mulshi region
Pages : 15-19 | 2266 Views | 261 Downloads
How to cite this article:
Rani B Bhagat, Mahadev Chambhare, Sandip Mate, Amit Dudhale, BN Zaware. Prospective wild edible fruit plants from part of northern Western Ghats (NWG), Mulshi (MS), India. J Med Plants Stud 2016;4(1):15-19.
Related Journal Subscription
Important Publications Links






