P-ISSN: 2394-0530, E-ISSN: 2320-3862
2016, Vol. 4, Issue 1, Part A
Curcumin reversion of neurochemical and immunohistochemical alterations in brain ischemia is related to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties
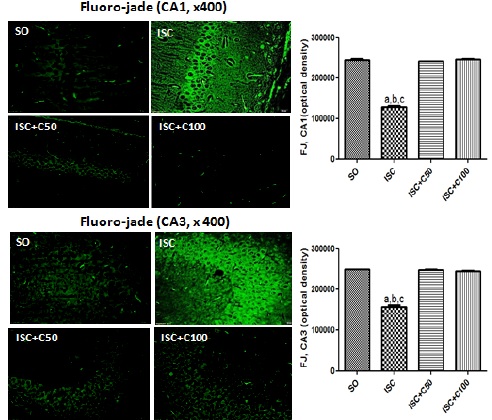
Fig.: Representative photomicrographs (magnification x400, scale bars=200 μm) of fluoro-jade staining in hippocampal CA1 and CA3 areas. The data were analyzed by the Image J software (NIH, USA). CA1: a. vs. SO, q=50.91; b. vs. ISC+C50, q=49.20; c. vs. ISC+C100, q=51.57; CA3: a. vs. SO, q=56.56; b. vs. ISC+C50, q=59.10; c. vs. ISC+C100, q=57.36. (One-way ANOVA and Tukey as the post hoc test).
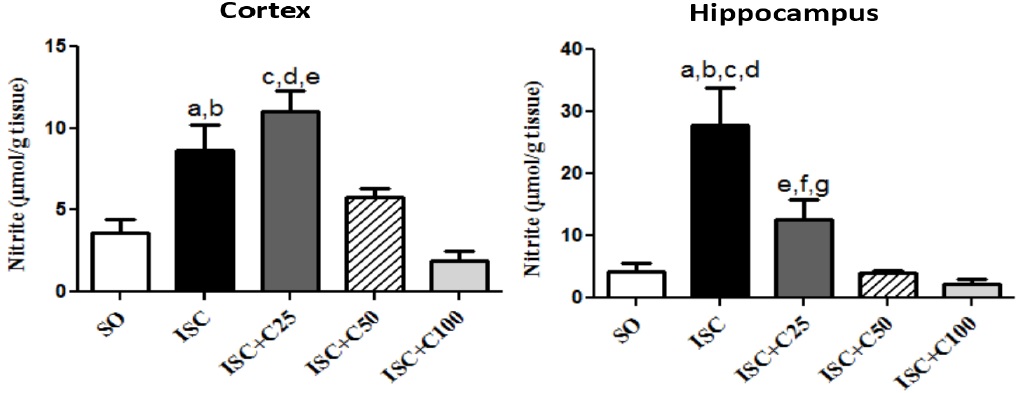
Fig.: Determination of nitrite contents in brain cortex and hippocampus from ischemic rat pups, at the 3rd post-ischemia day. Cortex: a. vs. SO, q=7.373; b. vs. ISC+C50, q=6.704; c. vs. ISC+C100, q=8.241. Hippocampus: a. vs. SO, q=7.811; b. vs. ISC+C25, q=4.458; c. vs. ISC+C50, q=8.110; d. vs. ISC+C100, q=8.612 (One-way ANOVA and Tukey as the post hoc test).
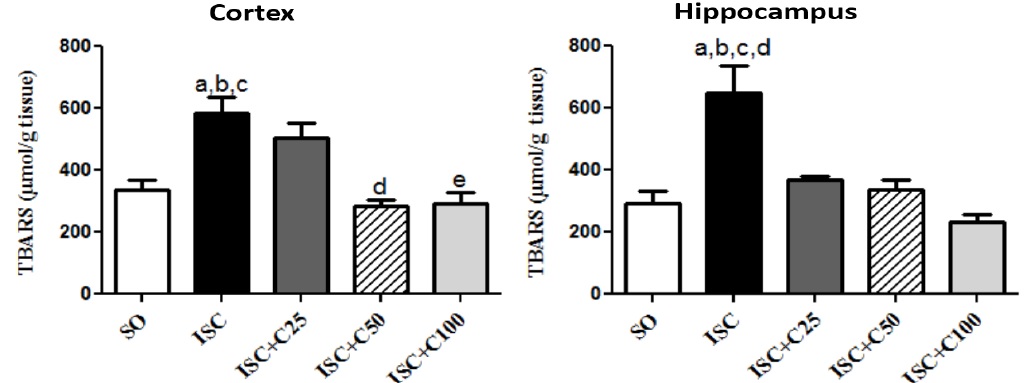
Fig.: Determination of lipid peroxidation (TBARS assay) in brain cortex and hippocampus from ischemic rat pups, at the 3rd post-ischemia day. Cortex: a. vs. SO, q=9.114; b. vs. ISC+C50, q=10.20; c. vs. ISC+C100, q=9.335; d. vs. ISC+C50, q=4.424. Hippocampus: a. vs. SO, q=8.058; b. vs. ISC+C25, q=5.265; c. vs. ISC+C50, q=7.143; d. vs. ISC+C100, q=7.863 (One-way ANOVA and Tukey as the post hoc test).
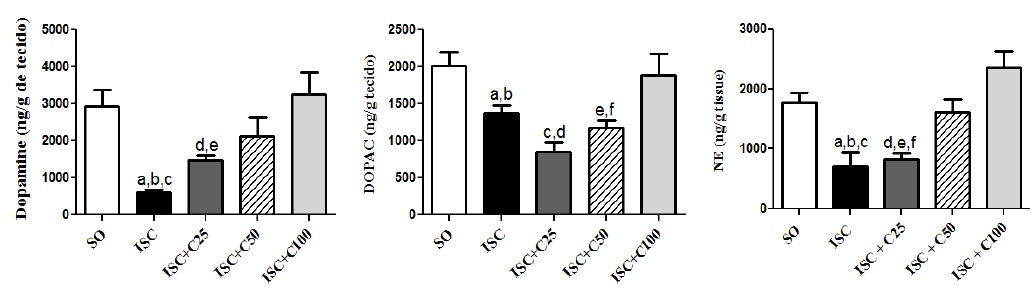
Fig.: Effects of curcumin on monoamine contents in striata from rat pups, at the 3rd post-ischemia day. DA: a. vs. SO, q=5.287; b. vs. ISC+C50, q=3.486; c. vs. ISC+C100, q=6.010; d. vs. ISC+C100, q=3.836. DOPAC: a. vs. SO, q=5.561; b. vs. ISC+C100, q=4.805; c. vs. SO, q=4.604; d. vs. ISC+C100, q=3.758; e. vs. SO, t=2.301. df=18, p=0.0336; f. vs. ISC+C25, t=3.214, df=12, p=0.074. NE: a. vs. SO, q=4.063; b. vs. ISC+C50, q=4.220; c. vs. ISC+C100, q=6.551; d. vs. SO, q=3.847; e. vs. ISC+C50, q=4.041; f. vs. ISC+C100, q=6.509 (One-way ANOVA and Newman-Keuls as the post hoc test).
Related Journal Subscription
Important Publications Links






