P-ISSN: 2394-0530, E-ISSN: 2320-3862
2013, Vol. 1, Issue 3, Part A
Salt Effects on Growth and Leaf Chemical Constituents ofrnSimmondsia chinensis (Link) Schneider
Hassan, F.A.S*, Bazaid. S., Ali. E.F (Egypt)
This study was conducted at Biology Department, Faculty of Science,Taif University, Saudi Arabia to investigaternthe effect of different salinity concentrations 8.6, 12.9, 17.2, 25.9, 34.5, 51.7, 86.2, 103.4 and 120.7 mM NaCl,rnbeside control treatment (tap water) on growth parameters, leaf measurements and leaf chemical constituents ofrnjojoba (Simmondsiachinensis (Link) Schneider). The results indicated that salinity treatments, especially the highestrnlevel significantly decreased plant height, number of both leaves and branches on the stem, as well as, the number ofrnnodes on the stem compared to other salinity treatments, in most cases. Similar trend has been observed for the leafrnmeasurements (length, width, area and stomatal density). The root parameters followed the same trend of shootrngrowth. Leaf chlorophyll content, protein, N, P, K and Ca were decreased with increasing salinity concentrations.rnMeanwhile, sodium, chloride and carbohydrates were gradually increased with increasing the concentration ofrnsalinity especially, with higher levels.
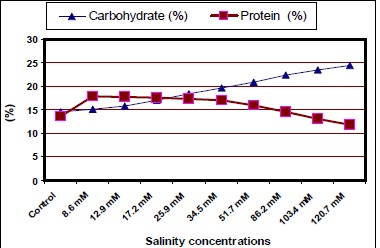
Fig.: Leaf content of carbohydrates of jojoba as affected by different salinity treatments
Pages : 22-34 | 1807 Views | 103 Downloads

How to cite this article:
Hassan, F.A.S*, Bazaid. S., Ali. E.F (Egypt). Salt Effects on Growth and Leaf Chemical Constituents ofrnSimmondsia chinensis (Link) Schneider. J Med Plants Stud 2013;1(3):22-34.
Related Journal Subscription
Important Publications Links






