P-ISSN: 2394-0530, E-ISSN: 2320-3862
2015, Vol. 3, Issue 5, Part B
Biochemical and molecular characterization on 11 cultivars of Coffea arabica L
Wael Taha Kasem, Atta E. M
The present studies are interested the chemotaxonomy including the phytochemical and molecular screening of the 11 cultivars of Coffea arabica obtained from Jazan, KSA. Total alkaloids, terpenoids, flavonoids, saponins were assessed and compared. Alkaloids and flavonoids are assayed by the method of thin layer chromatography (TLC). 14 phenolic compounds assayed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method. Seed protein diversity as reveled by variation in SDS-PAGE techniques been used as molecular methods. Statistical analysis of the phytochemical and the molecular data are analyzed separately and grouped using Minitab 17.0 statistical software. obtained statistical data resulted in two groups, the first includes cv. jazani, cv. Yemeni, cv. Chinese, cv. Colombian, cv. Habshi, cv. Yafi, cv. Indian, cv. Kenyan and cv. Brutte. The second group included the two cultivars of Ethiobian Harar and Brazilian. In the first group, three subgroups are recognized, cv. Yafi, cv. Yameni and cv. Jazani; the second subgroup included cv, Chinese, cv. Habshi and cv. Colombian meanwhile the third subgroup included the three cultivars of Indian, Kenyan and Brutte.
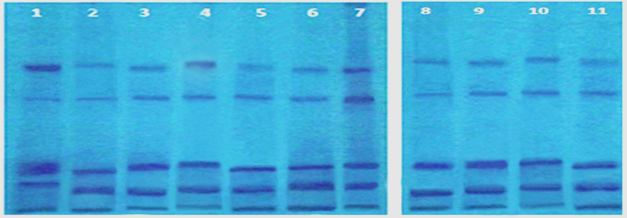
Fig.: Seed protein bands of Coffea arabica cultivars; 1- jazani, 2- Yemeni, 3-Chinese, 4- Colombian, 5- Habshi, 6- Yafi, 7- Ethiobian Harar, 8- Brazilian, 9- Indian, 10- Kenyan, 11- Brutte
Pages : 86-91 | 2039 Views | 227 Downloads

How to cite this article:
Wael Taha Kasem, Atta E. M. Biochemical and molecular characterization on 11 cultivars of Coffea arabica L. J Med Plants Stud 2015;3(5):86-91.
Related Journal Subscription
Important Publications Links






