P-ISSN: 2394-0530, E-ISSN: 2320-3862
2015, Vol. 3, Issue 5, Part B
Study of secondary metabolite constituents and curcumin contents of six different species of genus Curcuma
Bimal Dutta
Curcuma is a rhizomatous perennial plant which belongs to family Zingiberaceae having various ethnomedicinal significance. In this study, six different species of genus Curcuma i.e., C. amada, C. caesia, C. angustifolia, C. leucorrhiza, C. longa and C. zedoaria were screened for the presence of major secondary metabolites and curcumin contents were also analyzed. The dried and powdered rhizomes of each species were extracted with ethanol using Soxhlet extraction method. Phytochemical screening of ethanolic extracts of each species was performed qualitatively. Phytochemical screening of the ethanolic extract of six species showed the presence of phenols, flavonoids, alkaloids, terpenoids, tannins and saponins. Further, the curcumin contents of the ethanolic extracts of C. longa, C. zedoaria, C. angustifolia, C. leucorrhiza, C. amada and C. caesia were 125mg/100g, 88mg/100g, 71mg/100g, 15mg/100g, 11mg/100g and 8mg/100g of extract powder respectively.
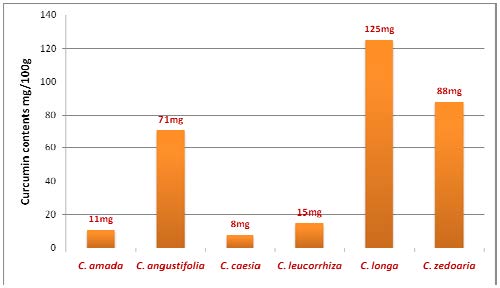
Fig.: Comparative analysis of curcumin contents in the six different species of Curcuma.
Pages : 116-119 | 3068 Views | 1132 Downloads

How to cite this article:
Bimal Dutta. Study of secondary metabolite constituents and curcumin contents of six different species of genus Curcuma. J Med Plants Stud 2015;3(5):116-119.
Related Journal Subscription
Important Publications Links






