P-ISSN: 2394-0530, E-ISSN: 2320-3862
2016, Vol. 4, Issue 2, Part B
Phytochemical studies and antibacterial activity of Decalepis hamiltonii Wight & Arn, an endangered medicinal plant
B Rajani, B Mohan, M Uma Devi, Ch. LP Shiva Kumari
Decalepis hamiltonii Wight & Arn. belongs to family Asclepiadaceae and commonly called as Maredu kommulu, Maredu gaddalu and Barre sugandhi. It is an endemic endangered climbing shrub and mostly all parts of the plant (root, stem and leaves) are medicinally used. Its tuberous roots are generally used as health drink mostly in the southern part of India and are well known for its medicinal properties. In the present investigation the presence of phytochemical constituents and antibacterial activity of the root, leaf and stem extracts of the plant are studied. Methonolic extract of different plant parts were obtained and assessed for the presence of various phytochemicals and antibacterial activity. These activities were determined by using standard protocols with some modifications. The phytochemical evaluation revealed the presence of Alkaloids, Flavonoids, Phenols, Steroids, Tannins, Terpenoids, Saponins and Glycosides. The antibacterial activity was observed against test organisms like Escherchia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumonia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The study supports the traditional usage of Decalepis hamiltonii and suggests that some of the plant extracts possess compounds with antimicrobial properties that can be used to develop in new drugs for the therapy of infectious diseases caused by pathogens.
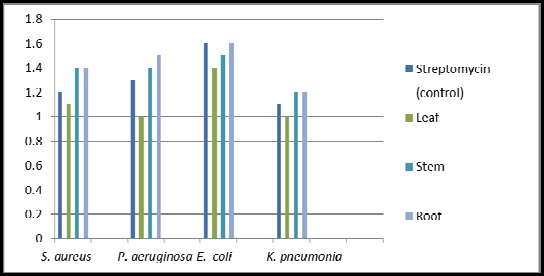
Fig.: Zone of inhibition with Methanolic Extract of Decalepis hamiltonii
Pages : 88-91 | 2357 Views | 262 Downloads

How to cite this article:
B Rajani, B Mohan, M Uma Devi, Ch. LP Shiva Kumari. Phytochemical studies and antibacterial activity of Decalepis hamiltonii Wight & Arn, an endangered medicinal plant. J Med Plants Stud 2016;4(2):88-91.
Related Journal Subscription
Important Publications Links






